Introduction
Minimal residual disease (MRD) has emerged as a critical prognostic marker in multiple myeloma (MM). Traditional MRD assessment relies heavily on bone marrow–based methods such as multiparameter flow cytometry (MFC), next-generation flow cytometry (NGF), and next-generation sequencing (NGS). However, these are invasive, costly, and limited in their ability to capture disease heterogeneity over time.
In this study, the authors evaluated EasyM, a mass spectrometry (MS)-based assay for blood-based MRD monitoring, offering a non-invasive and ultrasensitive alternative for longitudinal tracking of disease status in multiple myeloma.
Study Summary
447 sequential serum samples from 56 newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM) patients were assessed by EasyM clonotypic peptides mass spectrometry and the results compared to IFE, MFC (10-4), NGF (10-5) using time matched samples. Samples were obtained from a prospectively maintained institutional database of patients in China with multiple myeloma, the National Longitudinal Cohort of Hematological Diseases-Multiple Myeloma (NICHE-MM).
The objectives were to assess the sensitivity, specificity, and prognostic impact of EasyM in comparison to conventional MRD monitoring methods across a cohort of real-world patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM).
Key takeaways:
- EasyM showed 99.6% sensitivity vs IFE and 100% sensitivity vs both MFC and NGF.
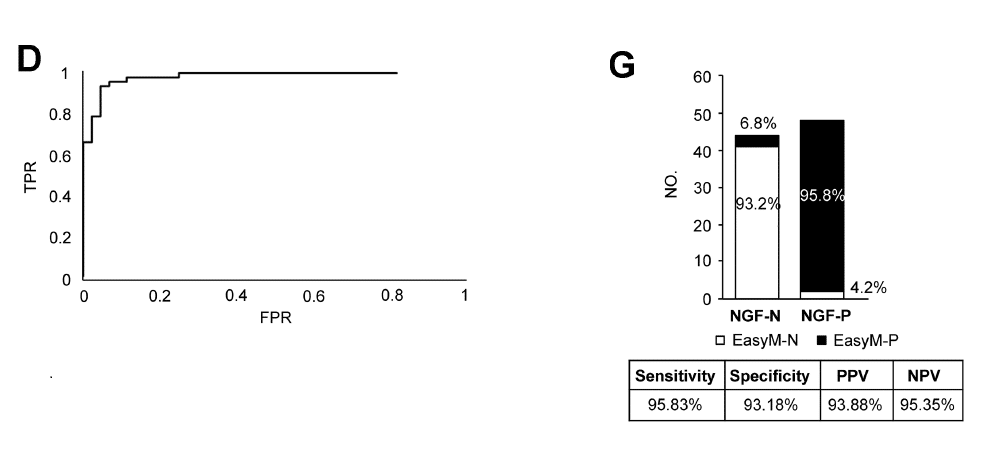
- When adjusted for an optimized cutoff (<1.86% residual M-protein), EasyM achieved specificity of 93.2% vs NGF, maintaining high sensitivity (93.2%).
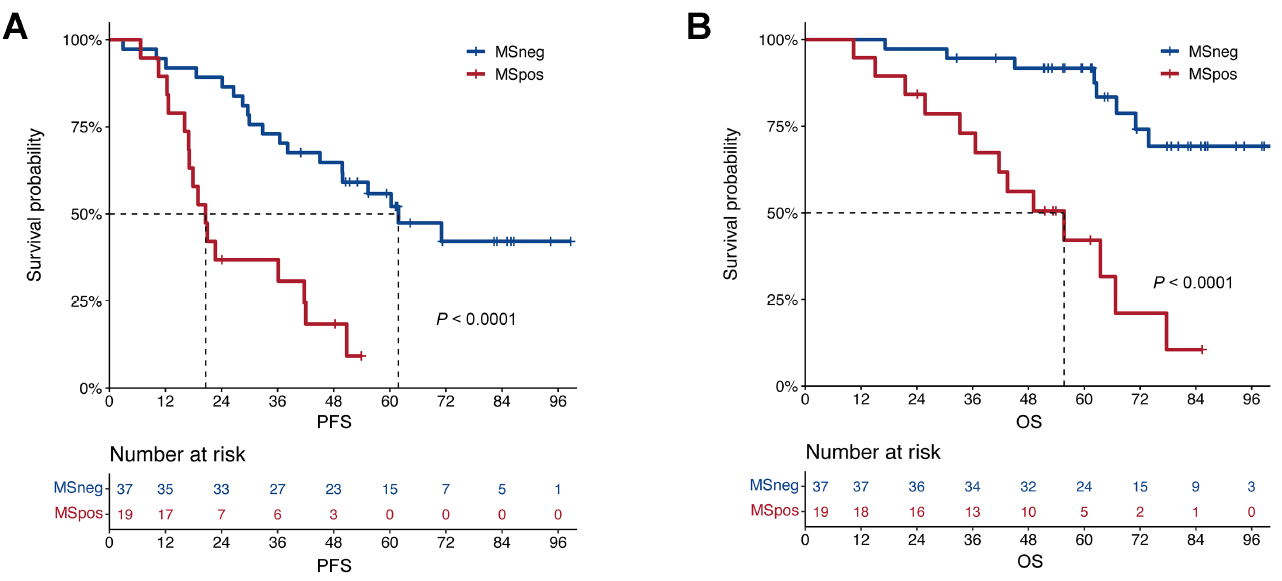
- MS-MRD negativity was independently predictive of significantly longer PFS and OS.
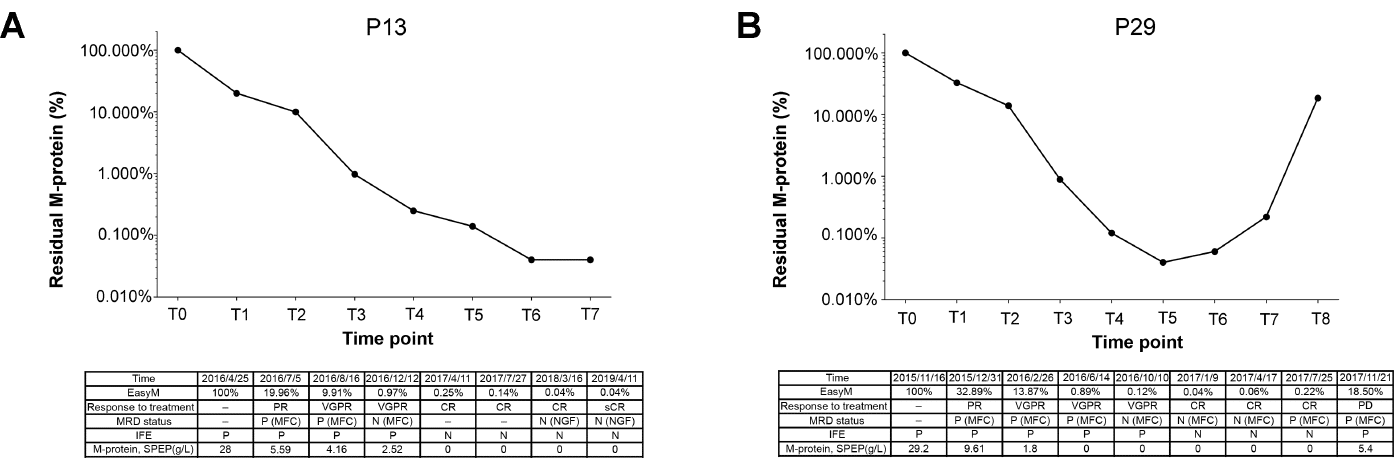
- EasyM enabled earlier relapse detection than IFE and bone marrow–based methods in several patients.
Conclusions
EasyM offers a minimally invasive, highly sensitive, and practical approach to MRD monitoring in MM. Its integration into clinical workflows could reduce the frequency of bone marrow biopsies and support more timely and personalized treatment adjustments.
Prognostic impact of EasyM MS-MRD
Prognostic impact of EasyM MS-MRD on [A] PFS and [B] OS by best MS-MRD status.
Longitudinal M-protein monitoring by EasyM
Longitudinal M-protein monitoring by EasyM [A] Patient 13 with deep response [B] Patient 29 showing relapse after achieving remission. Demonstrates how EasyM enables real-time monitoring for early detection of disease progression.
Comparison of EasyM and Bone Marrow NGF
[D] ROC analysis using NGF as the detection standard to establish a balanced EasyM negative cutoff value of <1.86% residual M-protein. [G] Comparison of EasyM and bone marrow NGF at EasyM MS negative cutoff <1.86% residual M-protein from time of first diagnosis.
Authors
Huishou Fan, Bing Wang, Lihui Shi, Ni Pan, Wenqiang Yan, Jingyu Xu, Lixin Gong, Lingna Li, Yuntong Liu, Chenxing Du, Jian Cui, Guoqing Zhu, Shuhui Deng, Weiwei Sui, Yan Xu, Shuhua Yi, Mu Hao, Dehui Zou, Xiequn Chen, Lugui Qiu, and Gang An
Contact Us.
We want to make an impact on myeloma.
We welcome discussion with academic investigators, pharmaceutical companies, patient groups and related service providers. Please reach out.
Talk to Our Scientists.
We Have Sequenced 5000+ Antibodies and We Are Eager to Help You.
Through next generation protein sequencing, Rapid Novor enables timely and reliable discovery and development of novel reagents, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Thanks to our Next Generation Protein Sequencing and antibody discovery services, researchers have furthered thousands of projects, patented antibody therapeutics, and ran the first recombinant polyclonal antibody diagnostics