Introduction
Here, we summarize a retrospective comparison of EasyM and Euroflow NGF for MRD in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients.
Minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity is a critical measure of therapeutic response in multiple myeloma (MM) and is strongly associated with improved progression-free and overall survival. The IMWG (International Myeloma Working Group) defines MRD negativity as the absence of clonal plasma cells in patients with multiple myeloma at a sensitivity threshold below 10-5 by either next-generation sequencing (NGS) or next-generation flow cytometry (NGF). However, both methods require invasive bone marrow biopsies which can often fail to capture the spatial heterogeneity of myeloma. New highly-sensitive mass spectrometry-based (MS) assays, such as EasyM (Rapid Novor), offer doctors a promising alternative to non-invasive MRD monitoring in the peripheral blood.
Study Summary
The 62 transplant eligible NDMM patients identified for the study were previously enrolled in the MM19 and MM21 clinical trials. All patients had a measurable M-protein >2 g/L by SPEP and/or FLC >100 mg/L at baseline.
Key Takeaways:
- EasyM MS analysis successfully identified clonotypic peptides in 92% (57/62) patients
- MS-negativity was achieved in 5% (3/62) of patients. All 3 patients who achieved MS-negativity remained in complete remission (CR) at 46-50 months post-ASCT
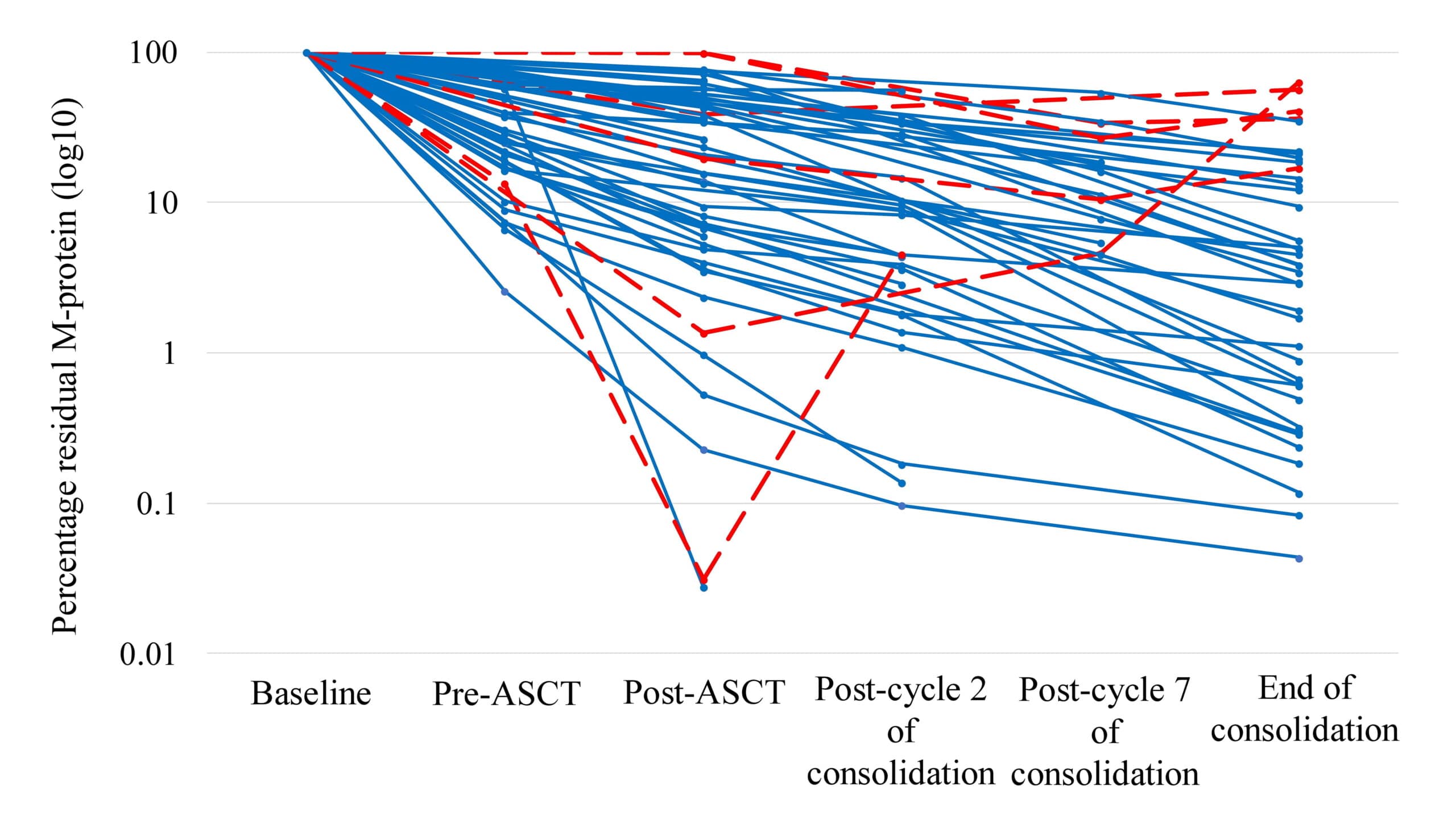
- Rising M-protein levels as measured by MS were observed in 6 patients, preceding relapse by 3 to 38 months. (Figure 1.)
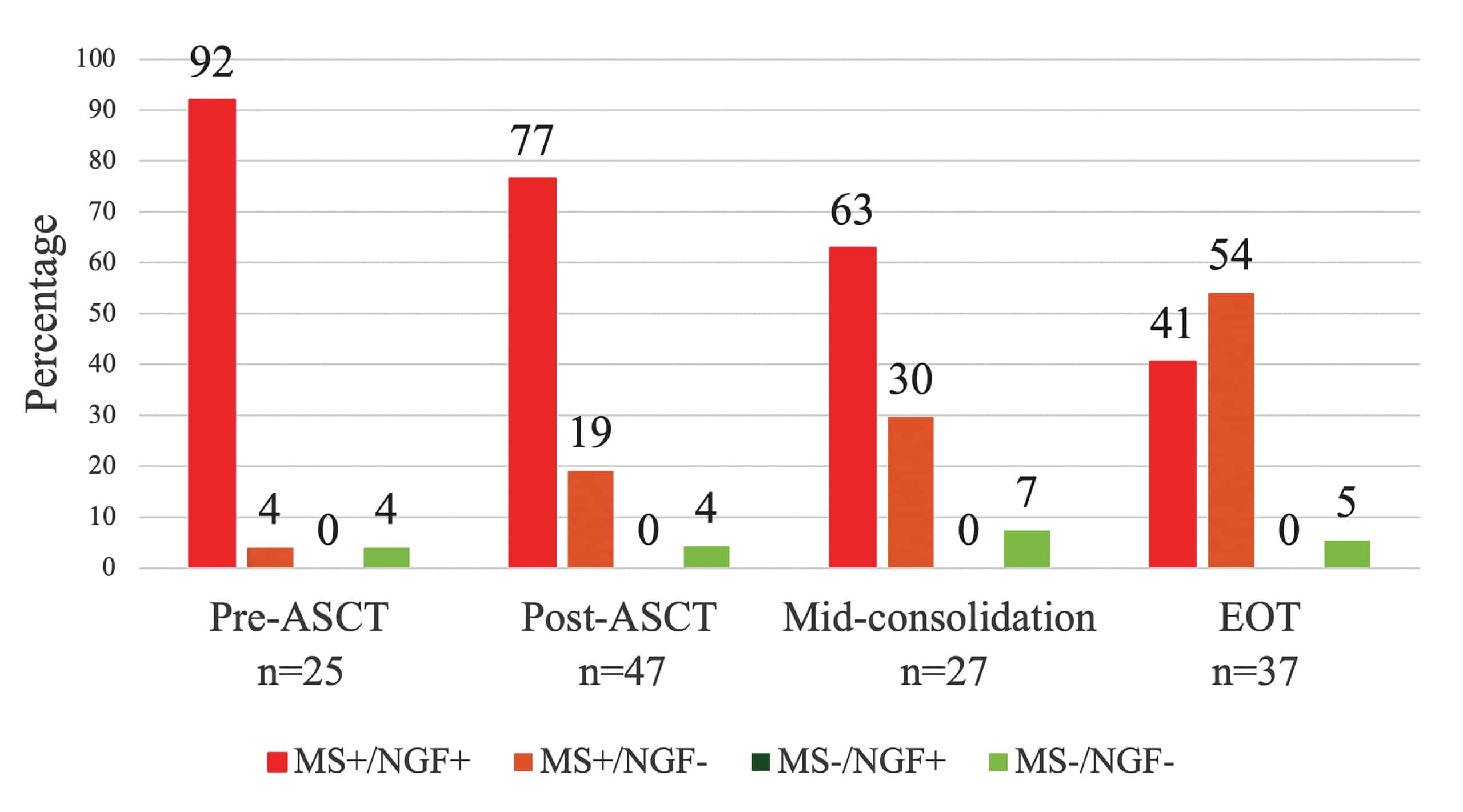
- Overall concordance between MS and NGF was 72% (98/136 samples). EasyM demonstrated greater sensitivity, detecting residual disease in 53% of NGF-negative samples. (Figure 2.)
- Discordance (EasyM+/NGF-) increased as patients progressed through therapy and into CR. This emphasizes EasyM’s increased sensitivity over NGF at later time points.
Figure 1. EasyM MRD kinetics in individual patients. Patients with rising EasyM are highlighted in red. ASCT, autologous stem cell transplantation; M-protein, monoclonal protein.
Figure 2. Matched MM MRD assessment by clonotypic peptides MS (EasyM) and NGF (EuroFlow platform). ASCT, autologous stem cell transplantation; EOT, end of therapy; MS, EasyM mass spectrometry; NGF, next-generation flow cytometry.
Conclusions
The study highlights the potential for new highly sensitive clonotypic peptides mass spectrometry assays to complement current BM-based MRD assessments in improving patient outcomes in MM:
- EasyM is non-invasive, addressing a major limitation of BM-based MRD tests and opening new opportunities for more frequent monitoring
- Early detection of rising M-protein levels by EasyM preceded relapse
.
Authors
Zhao J, Khong T, Gorniak M, Khaled A, McDonald Z, Reynolds J, Mithraprabhu S, Bingham N, Lim S, Wong D, Johnston A, Motorna O, Murphy N, Quach H, Yang L, Spencer A. Comparison of EasyM, a clonotypic mass spectrometry assay, and EuroFlow minimal residual disease assessment in multiple myeloma. Haematologica. Vol. 110 No. 3 (2025): March, 2025 https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2024.285933
Contact Us.
We want to make an impact on myeloma.
We welcome discussion with academic investigators, pharmaceutical companies, patient groups and related service providers. Please reach out.
Talk to Our Scientists.
We Have Sequenced 5000+ Antibodies and We Are Eager to Help You.
Through next generation protein sequencing, Rapid Novor enables timely and reliable discovery and development of novel reagents, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Thanks to our Next Generation Protein Sequencing and antibody discovery services, researchers have furthered thousands of projects, patented antibody therapeutics, and ran the first recombinant polyclonal antibody diagnostics